
(aplacophoran) |

(polyplacophoran) |
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA(Tree and traits from Nielson 1995 p. 111, and Brusca & Brusca 1990 p. 762) |
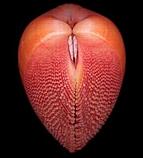
(heterodont bivalve) |

(scaphopods) |

(prosobranch gastropod) |
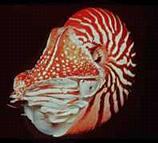
(nautiloid cephalopod) |

(aplacophoran) |

(polyplacophoran) |
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA(Tree and traits from Nielson 1995 p. 111, and Brusca & Brusca 1990 p. 762) |

(heterodont bivalve) |

(scaphopods) |

(prosobranch gastropod) |

(nautiloid cephalopod) |
======2================== Aplacophora (shell-less, worm-like molluscs)
|
<<=1===| ====4=============== Polyplacophora (chitons)
| |
==3==| ====6=========== Monoplacophora (primitive limpet-like molluscs)
| |
=5==| ===9== Gastropoda (snails, slugs, etc.)
| ==8==|
| | ==10== Cephalopoda (nautiloids, cuttlefish, squids, octopus)
==7==|
5="CONCHIFERA" | ==12== Bivalvia (mussels, clams, scallops, etc.)
==11=|
==13== Scaphopoda (tusk shells)
Back to Zool 250 version of tree for animal phyla or Protostomia.
|
b) mantle with calcareous spicules produced by single cells, c) posterolateral mantle cavity with multiple bipectinate gills (ctenidia) d) radula e) larval/adult body with traces of eight segments f) trochophore larvae** g) coelom via schizocoely** h) 'open' circulatory system (hemocoel) with pumping heart i) circumpharyngeal nerve-ring (brain) with ladder-like ventrolateral nerves** b) reduction/loss of foot & head c) reduced number of ctenidia (two or fewer) b) one or more dorsal, solid shell plates c) 8 pair pedal 'retractor' muscles d) mobile radular membrane & odontophore b) mantle girdle c) calcareous spicules from single cells** b) 3-layered shell (periostracum, prismatic & nacreous calcareous layers) c) crystalline style b) monopectinate ctenidia (5-6 pair) |
b) 1 or 2 pair ctenidia c) veliger larva (absent in Cephalopoda) b) dorsoventrally expanded body with large, dorsal viscera c) 1 pair pedal retractor muscles b) operculum attached to foot c) 1 pair ctenidia** b) shell with gas-filled chambers & siphuncle c) ink gland d) beak-like jaws e) large, circumoral tentacles/arms f) 'closed' circulatory system (vessels lined by epithelium) g) image-forming eyes & large brain b) burrowing foot c) paired, lateral larval shell plates d) 1 pair ctenidia** b) head lost c) enlarged mantle cavity & ctenidia d) mantle edge fused to shell e) byssal gland b) ctenidia lost c) captacula |