(acoel flatworm) |

(polyclad flatworm) |
PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES(Clade for classes and Turbellarian orders from Nielson 1995 p. 216.) |
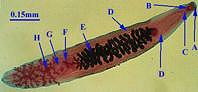
(trematode fluke) |

(cestode tapeworm head) |

(acoel flatworm) |

(polyclad flatworm) |
PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES(Clade for classes and Turbellarian orders from Nielson 1995 p. 216.) |

(trematode fluke) |

(cestode tapeworm head) |
Cl. TUR
==========2a======B=========== Or. Acoela (small body size, gutless)
<<=1===| E
| =======2c=======L========= Or. Polycladida (large body size, multi-branched gut)
=2b=| L
| ====2e========A======= Or. Tricladida (the planarians; 3-branched gut)
=2d=| R
| ==2g========IA==== Or. Rhabocoela (small body size, unbranched gut)
=2f=|
| ======4===== Cl. Trematoda (endoparasitic flukes)
==3===|
| ==6=== Cl. Monogenea (ectoparasites of aquatic vertebrates)
==5===|
==7=== Cl. Cestoidea (endoparasitic tapeworms)
Back to Zool 250 version of tree for animal phyla or Protostomia.
|
b) blind gut** c) protonephridia** d) coelom & blood vascular system absent** e) ciliated epidermis** f) multiciliated cells** g) epidermal gland cells extensive h) monociliated sperm i) hermaphroditic (unclear if valid trait) j) archoopheran reproductive system b) simple pharynx** c) lack protonephridia d) no distinct gonads (gametes from parenchyma) b) bi-ciliated sperm (present in all higher groups) c) gut cavity present d) plicate pharynx e) unique nucleotide triplet for Asparagine (Telford et al. 2000, PNAS 97:11359) b) pair of anterior tentacles (some) c) multiple gonads among branches of gut b) typical 'spiral' cleavage lost |
b) terminal mouth (also some rhabdocoels) c) paired intestinal cecae b) complex=indirect life cycle (1-2 intermediate hosts) c) anaerobic metabolism b) simple=direct life cycle** (no intermediate hosts) b) strobila (=chain of proglottids) c) mouth & gut absent d) reproductive system repeated in each proglottid e) complex=indirect life cycle (1 or more intermediate hosts) |