Biology 381
Pollution Biology
Department of Biological Sciences
University of Alberta
Edmonton, Alberta
 |
Biology 381 |
| 3. People, Population and Environment. |
3.1 Required reading and other announcements.
No assigned reading material. Interesting links to the World Wide Web are available.
3.2 Introduction.
People and population occupy a key position in Garret Hardin's Tragedy of the commons.
At what point does our population become so large that deterioration of environmental quality becomes a significant issue?

Decisions relating to population and environmental quality are going to have to reflect "value judgments".
3.3 World population is on the rise.
World Population (billions) 1950-2050
World population and projected population (medium variant) from 1950-2050. Data are expressed in billions of people.
http://www.undp.org/popin/wdtrends/pop/popcht1.htmOver the next 50 years, population growth is expected to bring the world population into range of 9 billion. Estimates are that population will stabilize at 11 billion around the year 2200.
Projections suggest that most of the increase (~98%) will occur in less developed regions of the world.
Populations for more developed regions appear to have stabilized.
While world population continues to grow, the rate of growth is expected to decline.
Average annual population increase (millions) 1950-2050
Average annual population increase and projected population increase (medium variant) from 1950-2050. Data are expressed in billions of people.
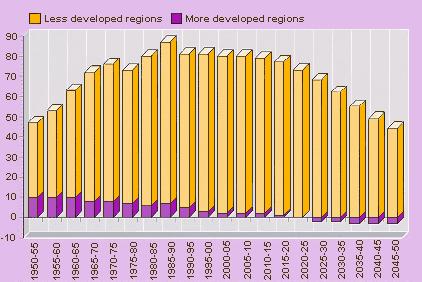
http://www.undp.org/popin/wdtrends/pop/popcht2.htm
http://www.prb.org/prb/images/tip10.jpg
http://www.prb.org/prb/media/tipquick.htm#tip3It is important to recognize that estimates such as this are speculative.
World population size according to the main fertility scenarios, 1950-2150.
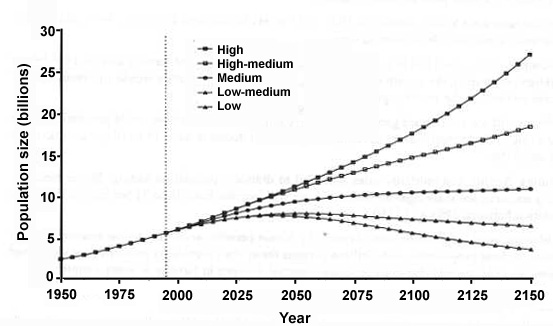
World population and projected population (5 fertility scenarios) 1950-2150. Data are expressed in billions of people.
http://www.undp.org/popin/wdtrends/execsum.htmThe bulk of population growth is occurring in urban areas. While rural populations continue to grow, estimates are that it will peak early in the new millenium.
Urban and rural populations (billions) 1950-2030.
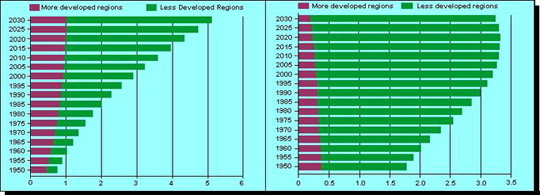
Population and projected population (1950-2030) of urban and rural regions.
Data are expressed in billions of people.
http://www.undp.org/popin/wdtrends/ura/uracht2.htm http://www.undp.org/popin/wdtrends/ura/uracht3.htmNumber of urban agglomerations with 1 million or more inhabitants (1950-2015).
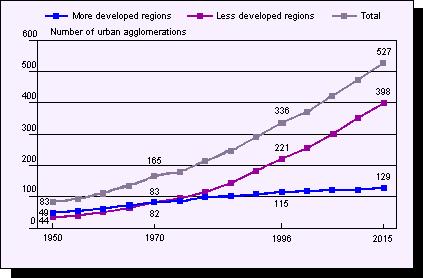
Number of urban agglomerations and projected number of urban agglomerations (1950-2015) with a million people or more.
http://www.undp.org/popin/wdtrends/urb/urbcht2.htmPercentage of population living in urban areas in 1996 and 2030.
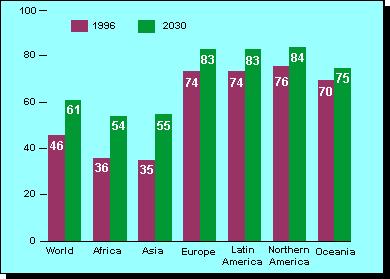
Percentage of population and projected percentage of population (medium variant) living in urban areas in 1996 and 2030.
http://www.undp.org/popin/wdtrends/ura/uracht1.htmDemographic data such as these provide a dramatic illustration of the population issue.
Many people have argued that population growth is an important issue because it essentially drives that aggregate environmental impact of human activities.
Does net environmental degradation have to grow in proportion with world population?
Should we mandate population or fertility control?

3.4 Feeding the billions...
Human beings have a right to adequate food or "food security" (International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, 1966).
In the past 25 years, extraordinary advances in agricultural productivity and public policy have provided more people with adequate food than ever before in history.
Agricultural production (top panel) and per capita agricultural production (bottom panel) in developed countries, developing countries, and the world. Data are expressed relative to 1980 (100%).
http://www.fao.org/wfs/wfsbook/e/ffa01-e.htmIncreases in agricultural productivity have reflected....
increased use of land for agriculture.
increased use of irrigation.
increased use of fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides.
development of high yielding crop cultivars.
reduced post-harvest losses.
Unfortunately, this food has not been uniformly available to all people.
Dietary energy supply per capita (1990/92) by country. Data are expressed in calories/day. A daily diet of 2200 calories is considered adequate to meet basic nutritional needs by the FAO/WHO.
http://www.fao.org/wfs/wfsbook/e/ffa01-e.htmFurthermore, population growth continues to increase faster than increases in food availability in many countries. Thus, hundreds of millions of people are unable to obtain sufficient food to support a healthy active life.
Total population and numbers of chronically undernourished people in developing countries (1990/92). Data are expressed in million of people.
http://www.fao.org/wfs/wfsbook/e/ffa01-e.htmDespite recent advances, a number of scientists have recently begun to raise concerns about global food security.
By the year 2050, our planetary resources will have to support an additional 3 billion people, and world food supply will have to be increased by 75% without destroying the natural resources on which production depends.
In recent years, growth in world agricultural production has slowed.
In 1996, world carryover stocks of grain fell to a low level of 51 days of consumption.This has led a number of analysts to speculate that we are beginning to approach what might be viewed as insurmountable production constraints. These constraints might include
a lack of prime land and water for conversion to agriculture.
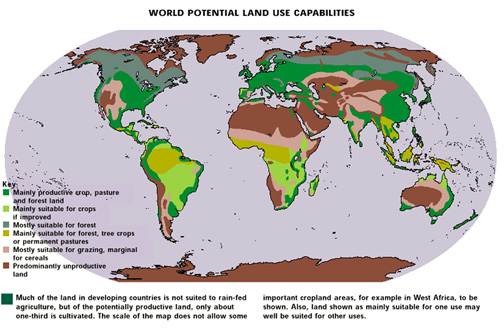
World potential land use capabilities. Large regions of the north, tropical Africa and Asia, central Australia, the western Americas and Antarctica are "predominantly unproductive land".
http://www.fao.org/wfs/wfsbook/e/ffa01-e.htm
Deterioration or erosion of soils. This results mainly from poor management practices. Soil erosion, nutrient depletion and salinization are a few of the more notable concerns here.
Soil degradation by geographical region and type. Data are expressed in millions of hectares. Water erosion is the major cause of degradation on all continents.
http://www.fao.org/wfs/wfsbook/e/ffa01-e.htm
increased resistance to pesticides and herbicides.
Numbers of species developing resistance to pesticides (1900-1990). More than 500 insects or mites have developed resistance. The number of plant diseases and weeds showing resistance is also increasing.
http://www.fao.org/wfs/wfsbook/e/ffa01-e.htm
increased impact of pollutants on agricultural productivity.
real biological constraints in plant productivity.
How would a potential food security crisis be addressed? A balance between reduced population growth and increased agricultural productivity.
Increased agricultural productivity will not come without a cost. Agriculture is a major source of environmental pollution.

Nutrient inputs in to aquatic ecosystems (soil erosion, nutrient laden runoff).
Ground water contamination (see above).
Herbicides and pesticides in the environment.
Animal wastes (gaseous, solid).
Metal contamination from fertilizers, fungicides, and use of sewage sludges.
Clearly, our agricultural systems will have to adapt to meet the growing demands of a growing population. Can it adapt quickly enough? How will our environment be affected?
3.5 Sustainability.
We are beginning to see ourselves more as part of an interactive global ecosystem. Success in maintaining the quality and productivity of our environment will depend on acknowledging this relationship and acting accordingly.
To deal with today's population and pollution issues, many scientists have advocated a holistic approach to environmental policy.
Environmental protection cannot be successfully accomplished in isolation from social and economic development.
3.6 Additional World Wide Web Information.
1997 world population overview. A summary of world population issues from the Population Institute.
World population at a glance. The U.S. Bureau of the Census provides a brief summary of the population issue.
World Population Projections to 2150. Projections of The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
Thirty largest countries ranked according to population size (1950, 1996, 2050). When does India become #1? Where is Canada?
Demographic Impact of HIV/AIDS. Will AIDS affect world population?
Food for All. A short book addressing the issue of global food security.
Canada's state of the environment report, 1996). Environmental issues from a Canadian perspective.